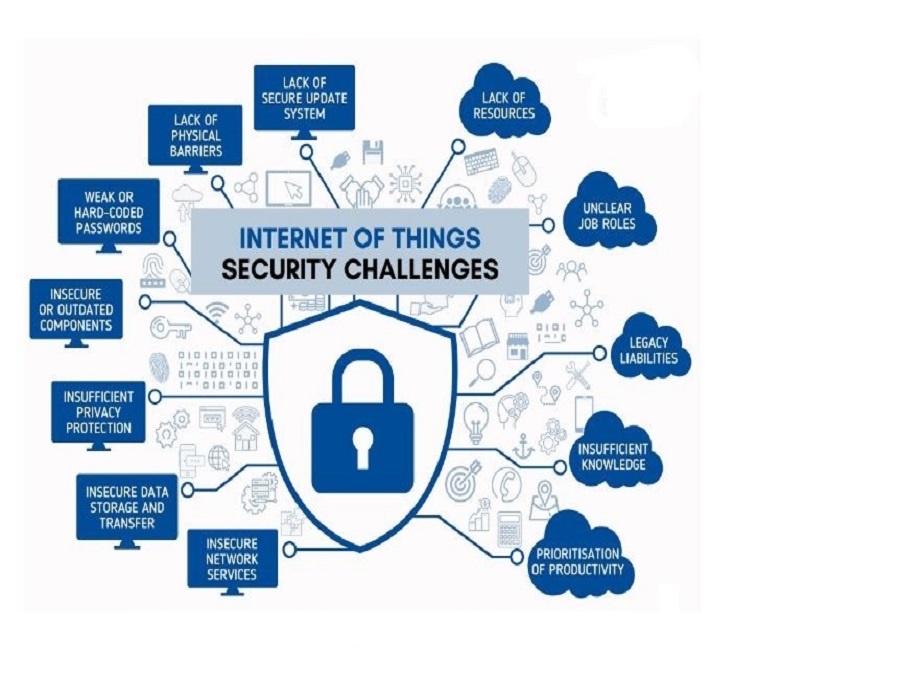
Introduction
The Internet of Things (IoT) has transformed the way we interact with technology, seamlessly integrating smart devices into our lives. While IoT devices offer unparalleled convenience, their proliferation has raised significant security concerns. Ensuring the security and privacy of IoT devices is paramount, as these interconnected devices are susceptible to cyber threats.
The security of these gadgets is an increasing problem as more and more devices are being connected to the internet. Cybercriminals are constantly seeking for methods to utilize flaws in IoT devices to access private information or damage people. IoT has a growing economic impact on society that has the ability to improve modern living standards and provide economic value. According to statistics, the IoT sector is boosting the world economy and adding value in astounding ways:
$5–12 trillion is anticipated to be distributed in 2030.In this blog, we will explore the essential steps and measures to enhance the security of IoT devices, safeguarding users and their data from potential risks.
Security for IoT is crucial
IoT is a fast growing network of actual physical objects like cars, appliances, and other household products that are linked to the internet, leaving them open to cyberattacks. Building a solid IoT security program is essential for security professionals as the number of connected devices rises. This program must incorporate best practices to safeguard these devices from illegal access and to safeguard critical data and assets. (Source URL: https://www.redhat.com/en/topics/security/security-for-iot-devices)
External Security
The IoT that connects to the network needs to be safe, but along with all of the sociological, environmental, and economic advantages, the quickly expanding connected world has also created a larger attack surface for adversaries to take advantage of. Only allowing reputable third-party IoT vendors is now one of the finest risk mitigation strategies for any firm.
Third party security guidelines for vendor risk management can assist avoid problematic IoT from being purchased in the first place given that not all in-house buyers are on the security team. Your third party risk management program, which contains the end-to-end security criteria the IoT provider needs to achieve for your digital supply chain security standards, can go into detail about these IoT provisions.
IoT devices gather and exchange a lot of data
Despite the fact that the majority of IoT devices today are not built for ongoing security, common vulnerabilities are being exploited for nefarious purposes. Many businesses who are unaware of what they have linked to the network suffer from disparate IoT and a lack of IoT asset inventory. In addition, when there are issues with home IoT, remote office issues also appear.
The essential steps to be followed for IoT security are
- Strong Authentication and Authorization:
Implementing robust authentication mechanisms is the first line of defense against unauthorized access. Multi-factor authentication and secure user credentials should be enforced to verify the identity of users and devices. Coupled with proper authorization policies, this ensures that only authorized entities can access sensitive data and functionalities. - Secure Communication:
Securing data in transit is vital to prevent data interception and eavesdropping. Employing strong encryption protocols like TLS (Transport Layer Security) ensures that data transmitted between IoT devices and the cloud remains encrypted, safeguarding it from potential threats during transmission. - Regular Firmware and Software Updates:
IoT devices must be updated regularly with the latest firmware and software patches. Promptly addressing security vulnerabilities and bugs through updates reduces the risk of exploitation by cyber attackers. - Secure Boot and Storage:
To prevent unauthorized tampering, devices should employ secure boot processes, ensuring that the software only starts from trusted sources. Additionally, sensitive data stored on IoT devices should be protected through encryption to prevent unauthorized access. - Disable Default Credentials:
Default credentials pose a significant risk, as attackers can exploit them to gain access to IoT devices. Disabling default credentials and enforcing strong, unique passwords during device setup is crucial to thwart potential attacks. - Network Segmentation:
Segmenting IoT devices from critical systems and sensitive data minimizes the impact of a potential breach. By restricting communication pathways, the attack surface is reduced, enhancing overall security. - Real-Time Monitoring and Anomaly Detection:
Deploying monitoring systems capable of identifying unusual activities in real-time is vital. Anomaly detection helps detect potential security breaches promptly, allowing for immediate mitigation actions. - Emphasize Privacy by Design:
Privacy considerations must be integral to the design and development of IoT devices. Limit data collection to essential information and anonymize data whenever possible to protect user privacy. - Comprehensive Security Testing:
Conduct rigorous security testing, including penetration testing and vulnerability assessments, to identify and rectify potential weaknesses. This proactive approach helps ensure robust security from the outset. - User Education:
Raising awareness among users about best security practices is critical. Educating users about potential risks and promoting secure behaviors fosters a safer IoT environment.
Conclusion
As IoT devices continue to enrich our lives, robust security measures are essential to protect users and their data from potential cyber threats. By adhering to the outlined steps and measures, manufacturers and users can contribute to an enhanced security posture for IoT devices. Emphasizing security at every stage of the IoT lifecycle will help create a connected world that is safe, secure, and resilient to evolving cyber challenges.