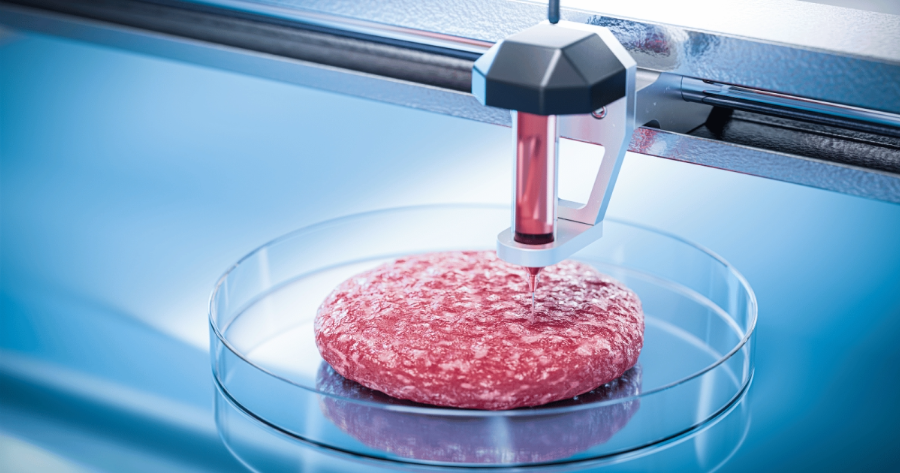
3D Printed Meat
The term “3D printed meat” describes the technique of producing edible food items that have the flavor and texture of conventional meat by employing 3D printing technology. This new technique has the ability to solve a number of issues related to traditional meat production including resource usage, animal welfare issues, and environmental effects.
Advantages Of 3D Printed Meat
To make a printable material that can be stacked to build a structure that resembles meat, a combination of plant-based or cultivated animal cells and other substances, such as fats, are usually used in the process. This approach has a number of possible benefits:
- Environmental Benefits: Traditional cattle production may have less environmental impact if meat is 3D printed. It might generate fewer greenhouse gas emissions and need fewer natural resources, such as land and water.
- Animal Welfare: Since 3D-printed meat doesn’t require the growing and killing of animals, it may help resolve moral dilemmas pertaining to animal welfare.
- Customization: With the exact control the technology provides over the meat’s composition, it may be possible to customize the meat’s flavor, texture, and nutritional value.
- Reduced Foodborne Illness: Compared to meat made normally, 3D-printed meat may have a lower risk of disease contamination because it is manufactured in a controlled environment.
Key Steps Involved in 3D Printed Meat
Tissue engineering, biochemistry, and 3D printing technology are just a few of the fields that come together to form the science behind 3D-printed meat. An outline of the main procedures and steps involved is provided below:
- Cell Sourcing
- Animals are used as the source of cells for lab-grown or cultured meat through biopsies. These cells include the myocytes (the muscle cells), the adipocytes (the fat cells), and other cell types that are involved in the composition of meat.
- Alternatively, the building blocks for meat substitutes can be found in plant-based proteins.
- Cell Culture Proliferation
- After being collected, the cells are cultivated in a controlled setting where they are given the circumstances, growth factors, and nutrition they need to multiply.
- Bioink Development
- To make a bioink for 3D printing, grown cells are combined with a biomaterial scaffold. The scaffold gives the cells the support and structure they require to arrange themselves into a three-dimensional structure.
- To boost nutritional value and replicate the flavor and texture of real meat, the bioink may also include additional ingredients such as vitamins, minerals, and plant-based proteins.
- 3D Printing Process
- To generate the appropriate flesh structure, the bioink is placed into a 3D printer and deposited layer by layer.
- A variety of 3D printing technologies, such as inkjet or extrusion-based printing, can be employed. The sort of cells to be used and the intended outcome determine which technology is best.
- Maturation and Tissue Formation
- The build goes through a maturation process following printing. This entails letting the cells proliferate and differentiate so they can create fat deposits and muscle tissues that resemble those in regular meat.
- Maturation circumstances include mechanical stimulation to support tissue organization, simulating the natural environment for muscle development.
- Harvesting and Processing
- After the meat from the 3D printer reaches maturity, it is harvested and turned into the finished product. To improve flavor and texture, extra processes including shape, seasoning, and cooking may be necessary.
To generate a product that closely resembles meat that is produced conventionally, the entire process strives to reproduce the complicated structure of traditional meat, including the arrangement of muscle fibers and fat. To enhance the flavor, consistency, and scalability of 3D-printed meat products, scientists and businesses are always improving these procedures.
Food Laws for 3D Printed Meat
- Safety and Labelling
Regulatory bodies usually evaluate innovative foods—including meat that has been 3D printed—for safety to make sure they adhere to set guidelines. Requirements for accurate and clear labeling are essential for educating customers about the nature of the product.
- Novel Food Approval
To guarantee they are safe for ingestion, innovative foods or food ingredients must undergo clearance procedures in many countries before they can be commercialized. Regulatory bodies might need comprehensive data regarding the ingredients, safety, and manufacturing procedure of 3D-printed meat.
- Biotechnology and Genetic Engineering Regulations
If the production process incorporates genetic engineering or biotechnology techniques, further rules can be applicable, based on the jurisdiction.
- Health and Nutritional Standards
Food products are frequently governed by health and nutritional regulations, including meat that has been 3D printed. These guidelines guarantee that goods don’t pose health dangers and fulfill the bare minimum of dietary requirements.
- Environmental and Ethical Considerations
Alternative meat production methods may give rise to ethical and environmental concerns that are taken into account by certain regulations.
Conclusion
With the introduction of 3D-printed meat, the field of food printing has witnessed a revolutionary advancement with enormous potential ramifications for the future of food production. This technology provides answers to urgent problems in traditional meat production, such as resource efficiency, animal welfare, and environmental sustainability. The potential to shape the future of our food supply through the use of plant-based or cultivated animal cells in conjunction with 3D printing techniques to construct structures resembling flesh creates new opportunities.
Source