Alzheimer’s Disease Prediction Using Deep Learning
Alzheimers.net was established in 2013 to provide caregivers and those who have the disease with a forum to discuss their enthusiasm for reform and treatment for the illness, according to the Alzheimers.net team. We are committed to providing support, education, and advocacy for anyone whose lives have been impacted by dementia, including Alzheimer’s disease.
The Mysterious Origins
The precise etiology of Alzheimer’s disease is among its deepest mysteries. The precise causes of this neurodegenerative condition have not been identified, despite much research and advances in neuroscience. While genetics may occasionally influence, other elements like environmental triggers and lifestyle decisions may also be involved. For preventive and early intervention, it is critical to discover the causes of the disease. Alzheimer’s disease risk can be predicted using deep learning algorithms. These models analyze a combination of clinical, genetic, and lifestyle data to predict an individual’s future risk of contracting the disease.
Genetics
- An increased chance of developing Alzheimer’s is associated with a family history of the disease, and early-onset Alzheimer’s has been associated with certain genetic variants.
- The most important risk factor is age. After the age of 65, there is a considerable increase in the risk of Alzheimer’s disease.
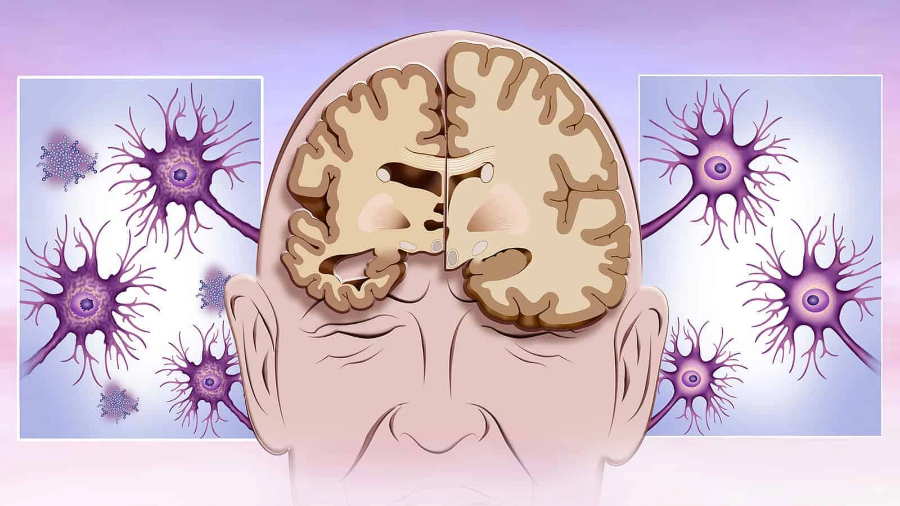
- Brain Alterations: Beta-amyloid plaques and tau tangles are aberrant protein deposits found in the brain of people with Alzheimer’s disease that impair cognitive performance.
Symptoms
- loss of memory, particularly for recent occurrences.
- difficulty with planning or problem-solving.
- uncertain of the time or location.
- difficulty executing routine chores.
- losing things.
- lower level of judgment.
Understanding Alzheimer’s Disease
- Alzheimer’s disease is investigated, along with the two machine learning (ML) techniques that aid in the early detection of the illness. A neurocognitive issue with early onset that affects people is Alzheimer’s disease.
- Alzheimer’s disease affects memory, thinking, and behavior and is a degenerative brain ailment. Dementia, a term used to describe a decrease in cognitive function severe enough to interfere with daily life, is most frequently caused by this. Alzheimer’s disease often starts with minor memory loss and can worsen to the point where sufferers are unable to identify and converse with their loved ones.
- The separation of the brain regions affected by AD into their neuroprotective and neurodegenerative components. It focuses on the pathomechanism, etiology, imaging modalities, biomarkers, and new treatment targets for Alzheimer’s disease.
- Developing more sophisticated treatments for AD requires early identification.
Description of deep learning
- Alzheimer’s disease is divided into three periods: the primary period, the intermediate period, and the last period of dementia. AD is diagnosed through brain monitoring modalities, such as CT (Computer Tomography) scan and PET (Positron Emission Tomography) scan resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging.
- This imaging method creates high-quality, high-resolution 2D and 3D images of brain regions by combining radio waves and magnetic fields. Neither radioactive tracers nor X-rays produce any hazardous radiation. Structural MRI, which analyses brain volumes in vivo to reveal brain deterioration, is the most often utilized MRI for instances of AD.
- Strong magnetic fields are used in the targeted region in an MRI scanner to produce structural magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), which can non-invasively offer precise information about the interior anatomical structure and morphology of brain tissues.
- Regular clinical outcome prediction is made possible by the EEG biomarkers. The precision of EEG-based psychophysiological indicators in forecasting patient outcomes.
- To track the development of mild cognitive impairment, the ADNI data set is utilized in conjunction with biological markers such as MRI, PET, and neuropsychological evaluations.
- Taking features out of the raw data is the first step. Uncontrolled neural layer networks and dispersed filtering are the techniques employed. Regression and sparse filtering are combined to create a softmax classification system for individuals. A few unsupervised learning strategies are employed to disseminate the gathered data, including scattered coding and Boltzmann machines.
Conclusion
Being a strong foe, Alzheimer’s disease affects not only those who have been diagnosed but also their families and caretakers. Even though there is no known cure, research into the causes and therapies for Alzheimer’s is moving forward quickly. Future prospects are brightened by developments in early detection, precision medication, and caregiver assistance. It is crucial to continue helping people with Alzheimer’s and the people who care about them on their difficult path up until a cure is discovered. To solve the riddles of this deadly disease, the scientific community must work together, raise awareness, and support further study. One of the main causes of death, particularly in affluent nations, is AD. Given how difficult it is to identify AD in clinics early on, using computer-based solutions in conjunction with medical professionals has much to offer regarding early identification. Deep learning has garnered much interest for this purpose in recent years.
Source
- https://www.bitsathy.ac.in/unraveling-the-links-between-alzheimers-disease-and-diabetes/
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/316764
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0933365722000975