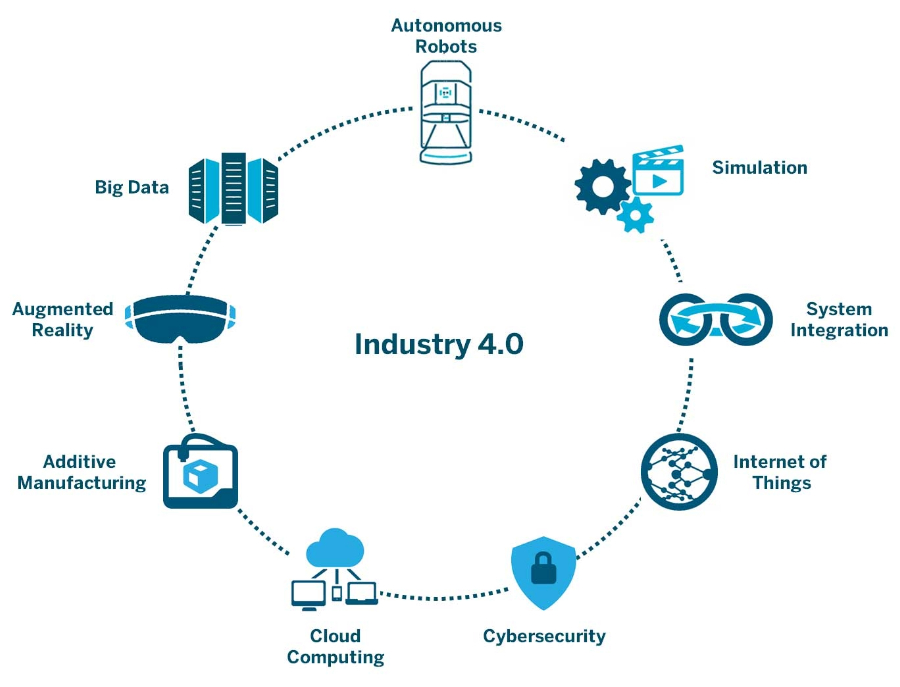
Industry 4.0 in Automation
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, Industry 4.0 has emerged as a transformative force, reshaping the way industries operate and pushing the boundaries of automation. This fourth industrial revolution is characterized by the integration of smart technologies, data analytics, and the Internet of Things (IoT) into manufacturing processes, creating a more interconnected and efficient ecosystem. In this blog, we will delve into the key components of Industry 4.0 and explore its impact on automation.
Understanding Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0, often referred to as the Fourth Industrial Revolution, represents a paradigm shift in manufacturing and automation. It is marked by the fusion of digital technologies with physical systems, resulting in a more intelligent and connected environment. The core components of Industry 4.0 include:
Internet of Things (IoT): The IoT plays a pivotal role in Industry 4.0 by connecting devices and machines to gather and exchange real-time data. This connectivity allows for better monitoring, control, and optimization of manufacturing processes.
Big Data and Analytics: The massive amounts of data generated by IoT devices are analyzed through advanced analytics tools. This data-driven approach provides valuable insights for decision-making, predictive maintenance, and process optimization.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML algorithms are employed to enhance automation systems, making them more adaptive and intelligent. These technologies enable machines to learn from experience, improving their performance over time.
Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS): CPS integrates the physical and digital worlds, creating a symbiotic relationship between machines and the virtual environment. This integration enhances communication, coordination, and decision-making across the manufacturing ecosystem.
Impact on Automation
Enhanced Efficiency: Industry 4.0 fosters automation systems that are not only capable of executing tasks but can also adapt to dynamic conditions. This adaptability results in increased efficiency, reduced downtime and enhanced overall productivity.
Predictive Maintenance: The integration of IoT and analytics enables predictive maintenance, allowing organizations to anticipate equipment failures before they occur. This proactive approach minimizes downtime and extends the lifespan of machinery.
Customization and Flexibility: Industry 4.0 facilitates the creation of more flexible and customizable production processes. Automation systems can be easily reconfigured to accommodate changes in product design or manufacturing requirements, providing a competitive edge in today’s fast-paced market.
Quality Improvement: Advanced analytics and real-time monitoring contribute to improved product quality. Automation systems can quickly detect and rectify defects, ensuring that the final products meet the highest standards.
Supply Chain Optimization: Industry 4.0 extends its impact beyond the factory floor to optimize the entire supply chain. Real-time data exchange enables better coordination between suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors, reducing lead times and improving overall efficiency.
Advancements in Industry 4.0 automation
5G Connectivity and Low-Latency Communication:
One of the significant advancements in Industry 4.0 is the integration of 5G connectivity. This ultra-fast, low-latency communication network facilitates real-time data exchange between devices, enabling quicker decision-making in automation systems. The enhanced speed and reliability of 5G contribute to more responsive and efficient industrial processes.
Robotics and Cobots (Collaborative Robots):
The latest generation of robots goes beyond mere automation. Collaborative robots, or cobots, are designed to work alongside humans, enhancing efficiency and safety on the factory floor. These robots can adapt to changes in their environment and collaborate seamlessly with human workers, opening new possibilities for flexible and dynamic manufacturing.
Blockchain for Supply Chain Transparency:
Blockchain technology has made inroads into Industry 4.0 by ensuring transparency and traceability in the supply chain. It provides an immutable and decentralized ledger that records transactions across the supply chain, reducing the risk of fraud and ensuring the authenticity of products. This is particularly valuable in industries where traceability and quality control are paramount.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR):
AR and VR are transforming how we design, train, and operate in manufacturing environments. AR overlays digital information onto the physical world, aiding in tasks such as maintenance and troubleshooting. VR, on the other hand, offers immersive training simulations and virtual walkthroughs of complex processes, enhancing training efficiency and minimizing errors.
Edge AI and Edge Computing:
Edge AI brings artificial intelligence capabilities to the edge of the network, allowing automation systems to make critical decisions without relying solely on cloud-based processing. This reduces latency, improves real-time responsiveness, and enhances the autonomy of machines in manufacturing processes.
Additive Manufacturing and 3D Printing:
The evolution of 3D printing and additive manufacturing has unlocked new possibilities in product design and prototyping. Industry 4.0 leverages these technologies to create complex, customized, and on-demand components, reducing waste and speeding up the product development cycle.
Digital Thread Integration:
The concept of a digital thread involves creating a seamless flow of data throughout the product lifecycle. From design and manufacturing to maintenance and end-of-life, a digital thread ensures that information is accessible and consistent across all stages, fostering better collaboration and decision-making.
Conclusion
As we navigate the era of Industry 4.0, automation is at the forefront of transformative change in the manufacturing landscape. The integration of IoT, AI, and analytics not only enhances operational efficiency but also opens new possibilities for innovation and competitiveness. Embracing these technological advancements is not just a choice but a necessity for industries looking to thrive in the dynamic and interconnected future of automation. The journey towards Industry 4.0 is a journey towards a smarter, more efficient, and agile future.
Source