Polyphenolics from Plants as Potential Medicine
Polyphenolics are the chemical compounds found in plants. These bioactive non-nutrient compounds are found in most of the fruits, vegetables, and grains consumed by humans in day-to-day life. Approximately 12,000 phytochemicals including tannins, terpenoids, flavones, saponins, steroids, and alkaloids have been identified so far but a large percentage still remains unexplored. Research studies over recent years claim that polyphenolics derived from plants play a major role in preventing chronic diseases. One major factor leading to chronic disease in humans is the production of excessive free radicals.
Free radicals and their impact
Free radicals are unstable molecules that can damage cells and tissues. They are produced naturally by the body, but they can also be caused by environmental factors such as pollution, smoking, and radiation.
When free radicals accumulate in the body, they can lead to a condition called oxidative stress. Oxidative stress can damage DNA, proteins, and lipids, and it is thought to play a role in the development of many chronic diseases, as in image:
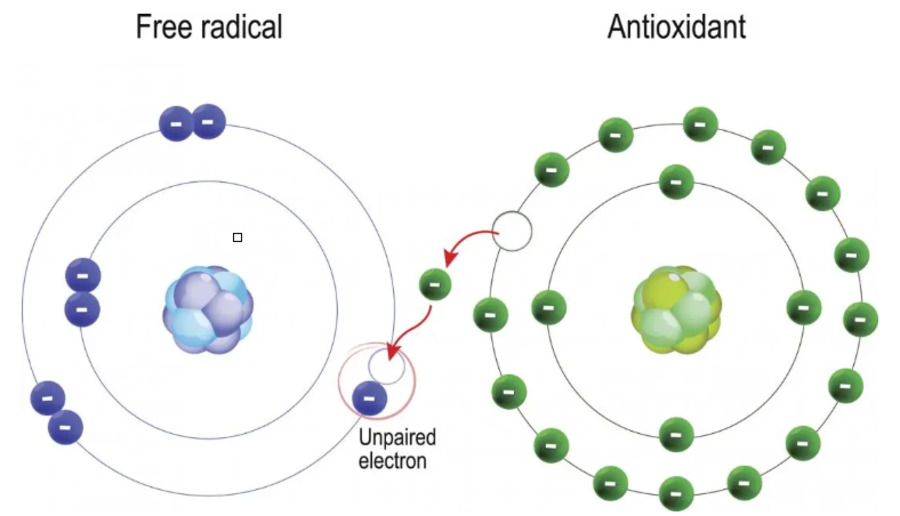
Scavenging free radicals
These free radicals can be scavenged by using antioxidants (such as polyphenolics) both from natural and synthetic sources. As free radicals are unstable, they take electrons from the antioxidants to make it stable (image 2). The unique feature of antioxidants is that they can donate an electron to free radicals thereby reducing their reactivity, without becoming reactive free radicals themselves.
These antioxidants are generally found in most of the food sources consumed by humans.
Greek physician Hippocrates (known as the father of medicine) claimed “Let food be your medicine”. After the pandemic in 2019, nutraceuticals have attracted considerable interest among researchers due to their therapeutic effects. Plant nutraceutical-based products in the form of pills, powders, liquids, and/or capsules are demonstrated to display a significant protective role against cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and cancer, postpone the aging process, and prevent chronic diseases thus increasing life expectancy.
Common sources of dietary polyphenols
Fruits: Oranges, apples, grapes, peaches, grapefruit juice, pomegranate juice, raspberries, strawberries, and apricots contain 200–300 mg polyphenols per 100 grams of fresh weight
Beverages: A cup of tea contains about 100 mg of polyphenols
Vegetables: One cup of spinach or shallot contains 40 mg of polyphenols. Broccoli has the largest content of polyphenols with 923 mg/100 g dry mass. Other vegetables such as cabbage, asparagus, carrots, etc., have good polyphenolic content
Whole grains: whole grain wheat, and oat flour
Nuts, seeds, and legumes: roasted soybeans, black beans, white beans, almonds, walnuts, flaxseed
Fats: Dark chocolate, virgin olive oil, sesame seed oil
Spices and seasonings: Turmeric, Cocoa powder, saffron, dried oregano, dried rosemary, soy sauce, cloves, star anise, celery seed, dried sage, dried spearmint, dried thyme, dried basil, curry powder, dried ginger, cumin, cinnamon
Polyphenolics from turmeric as medicine
Turmeric is a perennial plant native to Southeast Asia. It has been used for centuries in traditional medicine for its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antibacterial properties. Turmeric is also a popular spice in many cuisines, including Indian, Chinese, and Thai food.
In Southeast Asia, turmeric is used in religious ceremonies as well as in cooking. In Hindu culture, it is considered to be a sacred plant and is often used in wedding ceremonies and other religious rituals. It is also believed to have protective powers and is sometimes used to ward off evil spirits.
Here are some of the health benefits of turmeric
Reduces inflammation: Turmeric contains curcumin, a compound that has powerful anti-inflammatory properties. This can help to relieve pain and swelling associated with conditions such as arthritis, muscle pain, and inflammatory bowel disease.
Improves cognitive function: Turmeric may help to improve cognitive function by reducing inflammation and protecting brain cells from damage. This can help to improve memory, focus, and learning.
Boosts the immune system: Turmeric has been shown to boost the immune system by stimulating the production of white blood cells. This can help to fight off infections and diseases.
Protects against cancer: Turmeric has been shown to have cancer-fighting properties. It may help to prevent the growth and spread of cancer cells.
Improves heart health: Turmeric may help to improve heart health by reducing cholesterol levels and blood pressure. It may also help to protect against heart disease and stroke.
Discussion
Polyphenolics from plants act as a potential free radical scavenger. These polyphenolics are found in most of the food sources consumed but the composition varies depending on the source and how it is processed. It is important to note that not all polyphenols display the same effect on humans. Some are more potent antioxidants/medicines than others. Polyphenolic-rich food incorporated into the diet will boost the immune system and help substantially in the prevention of chronic diseases.
Source:
- https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/polyphenols
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/319728
- https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/top-10-evidence-based-health-benefits-of-turmeric