Wideband Radio Monitoring Module with Wireless Energy Harvesting
In our ever-connected world, the demand for efficient and reliable wireless communication systems is burgeoning. Wideband radio monitoring modules have emerged as pivotal tools in this landscape, enabling the surveillance and analysis of various wireless signals across a broad spectrum. But what if these modules could not only monitor but also sustain themselves through innovative energy-harvesting techniques? Enter the realm of wireless energy harvesting, a groundbreaking concept poised to revolutionize the way we power our devices. In this blog, we’ll delve into the intricacies of wideband radio monitoring modules coupled with wireless energy harvesting, exploring its potential through case studies, practical examples, and glimpses into the future. Wideband radio monitoring modules serve as the eyes and ears of modern communication networks. These modules are adept at scanning vast frequency ranges and detecting signals from various sources including Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, cellular networks, and more. They play a crucial role in spectrum management, security enforcement, and interference mitigation. Traditionally, these modules rely on conventional power sources such as batteries or grid electricity, limiting their deployment in remote or inaccessible areas.
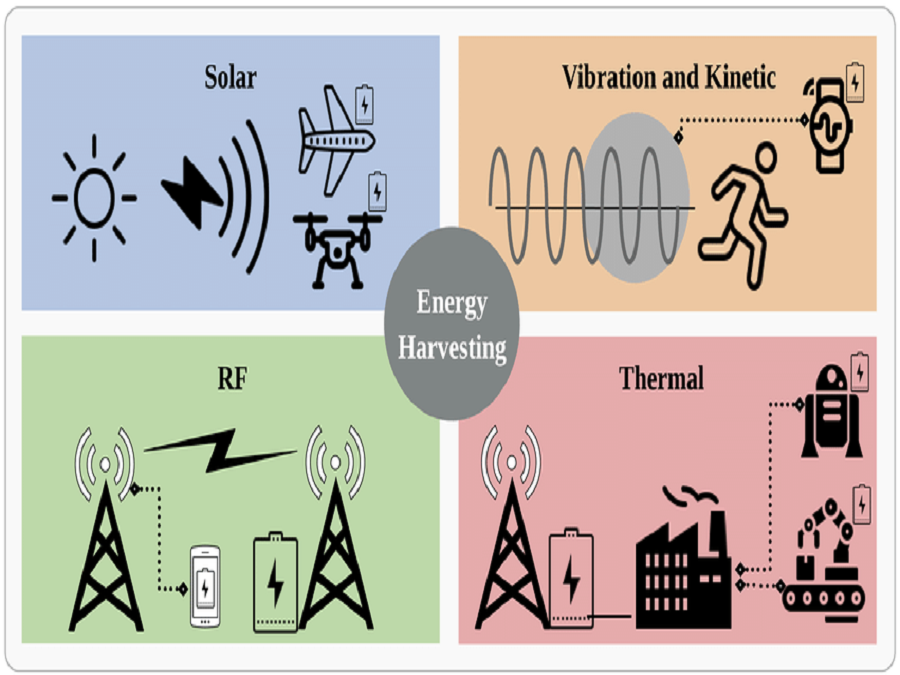
Wireless energy harvesting offers a compelling solution to the power conundrum faced by monitoring modules. By harnessing ambient energy from the environment, these modules can operate autonomously, eliminating the need for frequent battery replacements or wired connections. This concept taps into various energy sources such as solar radiation, radiofrequency (RF) signals, vibrational energy, and thermal differentials, converting them into usable electrical power. Imagine a wideband monitoring module equipped with solar panels. Installed atop a communication tower or an IoT device, these panels harvest sunlight throughout the day, converting it into electrical energy to power the module. This setup ensures uninterrupted operation even in remote locations without access to conventional power sources. In bustling urban environments teeming with wireless signals, RF energy harvesting presents an intriguing opportunity. Wideband monitoring modules equipped with RF harvesting antennas can scavenge energy from ambient Wi-Fi, cellular, and other RF transmissions. This concept enables sustainable operation in densely populated areas where energy sources are abundant.
For mobile deployments such as wearable monitoring devices or portable spectrum analyzers, vibrational energy harvesting proves invaluable. Utilizing piezoelectric or electromagnetic transducers, these modules can convert mechanical vibrations from motion or machinery into electrical power. This innovation extends the battery life of mobile monitoring units, enhancing their usability and efficiency. The integration of wireless energy harvesting into wideband radio monitoring modules heralds a new era of sustainability and autonomy in wireless communication systems. By reducing dependency on conventional power sources and mitigating environmental impact, this technology paves the way for a more resilient and eco-friendly infrastructure. Furthermore, it facilitates the deployment of monitoring solutions in challenging environments, empowering industries such as telecommunications, IoT, and defense with unprecedented capabilities.
As we look ahead, the potential applications of wideband monitoring modules with wireless energy harvesting are limitless. From smart cities and industrial automation to environmental monitoring and disaster management, these systems promise to reshape the way we interact with our surroundings. Moreover, ongoing advancements in energy-harvesting technologies, coupled with miniaturization and optimization efforts, will drive further innovation and adoption in this field. In conclusion, the convergence of wideband radio monitoring modules with wireless energy harvesting represents a paradigm shift in wireless communication and energy sustainability. Through case studies, practical examples, and a forward-looking perspective, we’ve glimpsed into the transformative potential of this synergy. As we continue to explore and refine these technologies, we inch closer to a future where wireless connectivity is not only ubiquitous but also environmentally conscious and self-sustaining.
Looking ahead, the integration of wireless energy harvesting into wideband monitoring modules holds promise for addressing some of the most pressing challenges of our time. Imagine networks of autonomous sensors powered by renewable energy, monitoring air quality, detecting environmental hazards, and optimizing resource utilization in real time. Envision smart agricultural systems that leverage energy harvested from the sun and the wind to monitor crop health and manage irrigation. Picture remote communities empowered by off-grid communication networks sustained by the natural energy sources surrounding them. As these technologies mature and become more accessible, they will catalyze innovation across industries, driving the development of sustainable solutions to complex problems. Moreover, they will empower communities around the world with the tools they need to thrive in an increasingly interconnected and dynamic environment. By embracing the possibilities offered by wideband radio monitoring modules with wireless energy harvesting, we embark on a journey toward a brighter, greener, and more resilient future.
Source